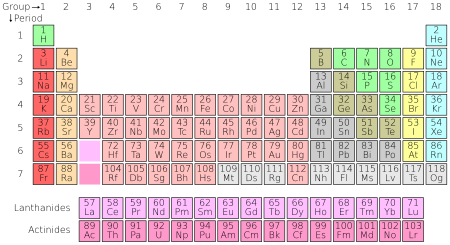
MODERN PERIODIC TABLE
In 1869 Russian chemist Dimitri Mendeleev started the development of the periodic table, arranging chemical elements by atomic mass.
He predicted the discovery of other elements, and left spaces open in his periodic table for them.
Dmitri Mendeleev, a Siberian-born Russian chemist, was the first scientist to make a periodic table much like the one we use today. Mendeleev arranged the elements in a table ordered by atomic weight, corresponding to relative molar mass as defined today.
· Before 1800 (36 elements): discoveries during and before the
Enlightenment.
· 1800-1849 (+22 elements): impulse from scientific (empirical processes
systematization and modern atomic theory) and industrial revolutions.
· 1850-1899 (+23 elements): the age of classifying elements received an
impulse from the spectrum analysis. Boisbaudran, Bunsen, Crookes,
Kirchhoff, and others "hunting emission line signatures".
· 1900-1949 (+13 elements): impulse from the old quantum theory, the
consolidated periodic table, and quantum mechanics.
· 1950-1999 (+15 elements): "atomic bomb" and Particle physics issues, for
atomic numbers 97 and above.
PERIODS:
It tells about how many energy level an atom has.
Horizontal rows of the periodic table.
GROUPS/FAMILIES: Vertical columns of the periodic table.
Group- last electron configuration
Family- states the common properties
**the elements in any group of the periodic table have physical and chemical properties. **
Today's Periodic Table
The most important difference between Mendeleev's table and today's table is the modern table is organized by increasing atomic number, not increasing atomic weight. Why was the table changed? In 1914, Henry Moseley learned you could experimentally determine the atomic numbers of elements. Before that, atomic numbers were just the order of elements based on increasing atomic weight. Once atomic numbers had significance, the periodic table was reorganized.
Dianne Ang
Androse Ansaldo
Micah Antonio
Oya Bautista
Angela Cansana
No comments:
Post a Comment