ELECTRONEGATIVITY
-is a chemical property that describes the ability of an atom (or, more rarely, a functional group) to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself.
-An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance that its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus.
-Electronegativity, as it is usually calculated, is not strictly an atomic property, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule.
-Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons.
-A large electronegativity difference leads to an ionic bond.
-Electronegative elements tend to gain electrons to become anionic Lewis bases.
-An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance that its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus.
-Electronegativity, as it is usually calculated, is not strictly an atomic property, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule.
-Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons.
-A large electronegativity difference leads to an ionic bond.
-Electronegative elements tend to gain electrons to become anionic Lewis bases.
ATOMIC RADIUS
-The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atoms, usually the mean or typical distance from the nucleus to the boundary of the surrounding cloud of electrons. ...
-Moving from left to right across a period, electrons are added one at a time to the outer energy shell.
-Moving from left to right across a period, electrons are added one at a time to the outer energy shell.
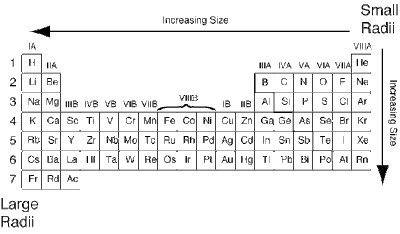
ATOMIC RADIUS PERIODIC TREND
As you move from right to left and up to down, the atomic radius increases. In short, the element in the bottom most part of the left side has the largest atom
Now let's try some exercises! \:D/
Arrange the following from lowest to highest
1. Be, Ar, Ne, Ge
2. Fr, Cs, Ba, Ra
3. Os, Cu, Zn, Re
4. Ag, Xe, Ge, Rb
MEMBERS:
Racadio
Ramiento
Rariza
Reyes
Rimando
Resources:
-http://www.chem.fsu.edu/chemlab/chm1050lmanual/halogens/enegtrend.jpg
-http://www.iun.edu/~cpanhd/C101webnotes/modern-atomic-theory/images/
atomic-radii.jpg
-http://www.grandinetti.org/Teaching/Chem121/Lectures/AtomicRadii/assets/radiitable.gif-http://www.grandinetti.org/Teaching/Chem121/Lectures/AtomicRadii/assets/radiitable.gif
www.grandinetti.org
-http://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/36_eneg/electroneg.htmlwww.grandinetti.org
-http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/E/Electronegativity.html


No comments:
Post a Comment